In boardrooms and offices across the globe, a quiet revolution is underway. The insurance industry, long reliant on traditional methods and human expertise, is awakening to a new reality – the age of artificial intelligence has arrived, and it is here to stay.
From the bustling streets of New York to the tech hubs of Silicon Valley, insurers are embracing the power of machine learning and data analytics to transform every facet of their operations.
These algorithmic entities are the insurance industry’s secret weapon. They crunch numbers, spot patterns, and identify risks and opportunities with unparalleled speed and accuracy. They are not just speeding things up but making the entire process smarter. By analyzing vast troves of data, they detect fraud faster than a detective and predict future claims with eerie precision. The best part? These AI-powered helpers benefit both insurers and policyholders.
So buckle up, insurance professionals – the future is coming. Let us look at how AI/ML are transforming insurance because the days of business as usual are officially over.
The Explosion of Data from Connected Devices
The insurance industry is witnessing an unprecedented influx of data, largely driven by the rapid adoption of connected devices. These devices, including smartphones, smart homes, telematics devices, and wearables, generate vast amounts of data that provide granular insights into policyholder behavior and risk profiles.
This explosion of data is the foundation upon which various AI-driven insurance applications are built.
Telematics Devices and Usage-Based Insurance
One prominent example of how connected devices transform insurance is the rise of usage-based insurance (UBI) programs. By leveraging data from telematics devices installed in vehicles, insurers can track driving behavior, such as speed, acceleration, and braking patterns, to assess the risk profile of individual drivers.
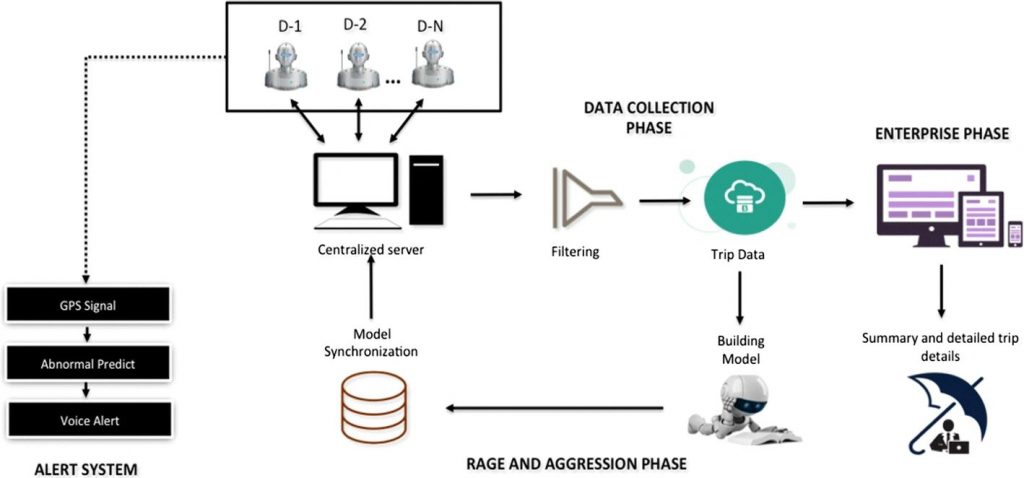
Proposed solution for personalized premium calculation
This data enables insurers to offer more personalized and accurate pricing based on actual driving habits rather than relying solely on traditional factors like age, gender, and credit score. Moreover, the continuous stream of data from telematics devices allows insurers to update risk assessments in real-time, enabling dynamic pricing adjustments based on changes in driving behavior.
Wearables and Health Data Analytics
In the health and life insurance sectors, wearable devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches are providing insurers with valuable data on policyholders’ health and lifestyle habits. By analyzing data on physical activity, sleep patterns, and other biometric indicators, insurers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s health risks.
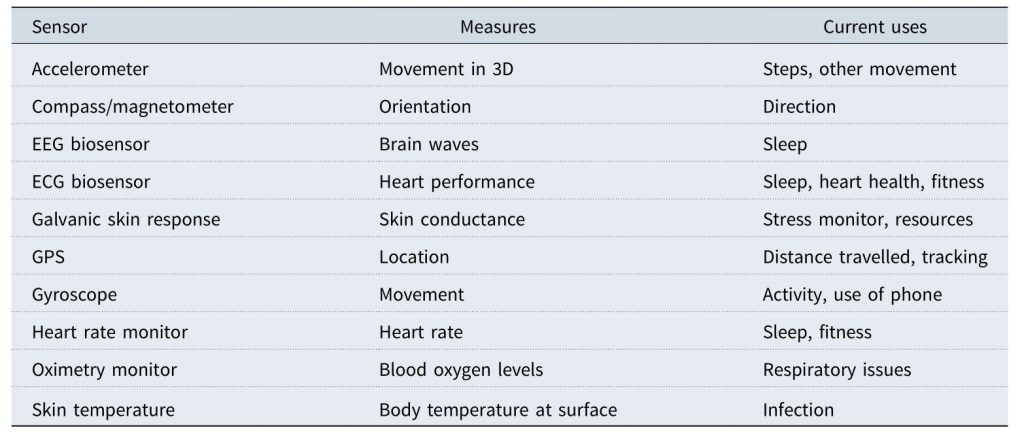
Sensors in wearable technology
This data can be fed into predictive analytics models to identify potential health issues early on, enabling insurers to offer proactive interventions and personalized wellness programs.
Open-Source Data Ecosystems and Augmented Risk Assessment
The explosion of data from connected devices is not limited to the data generated by policyholders themselves. The rise of open-source data ecosystems, including public records, social media feeds, and other external data sources, provides insurers with additional context to augment their risk assessments.
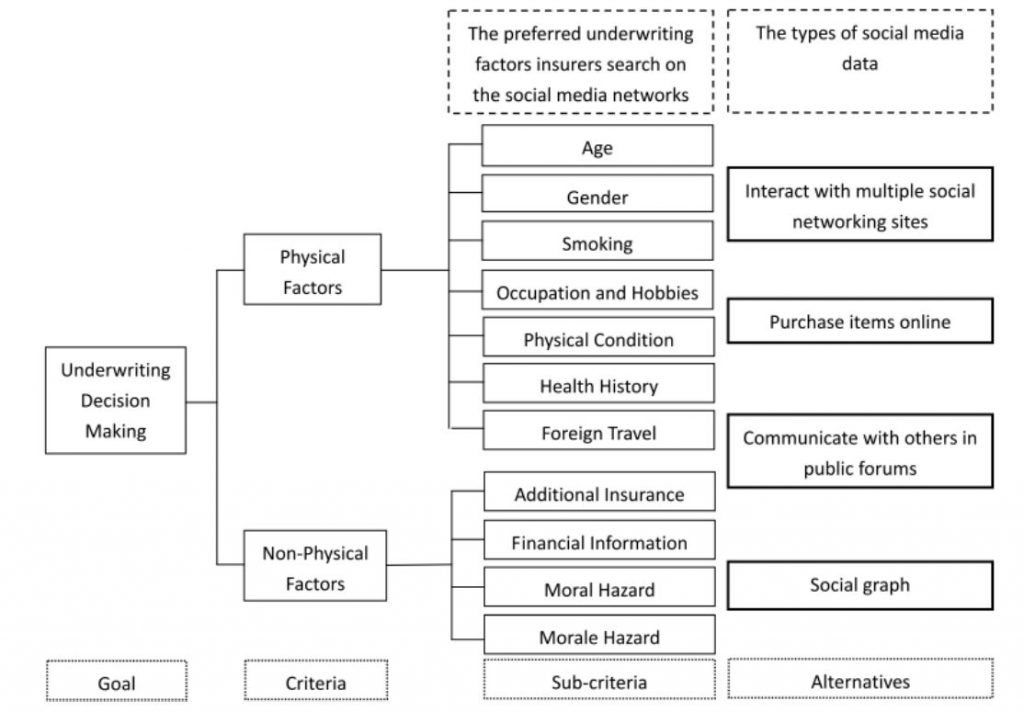
Underwriting hierarchy using social media
Social media data can provide insights into a policyholder’s lifestyle habits and risk behaviors, while public records can reveal potential red flags like past bankruptcies or criminal convictions.
Predictive Analytics and Pension Risk Transfer
The explosion of data from connected devices is also transforming the Pension Risk Transfer (PRT) space.
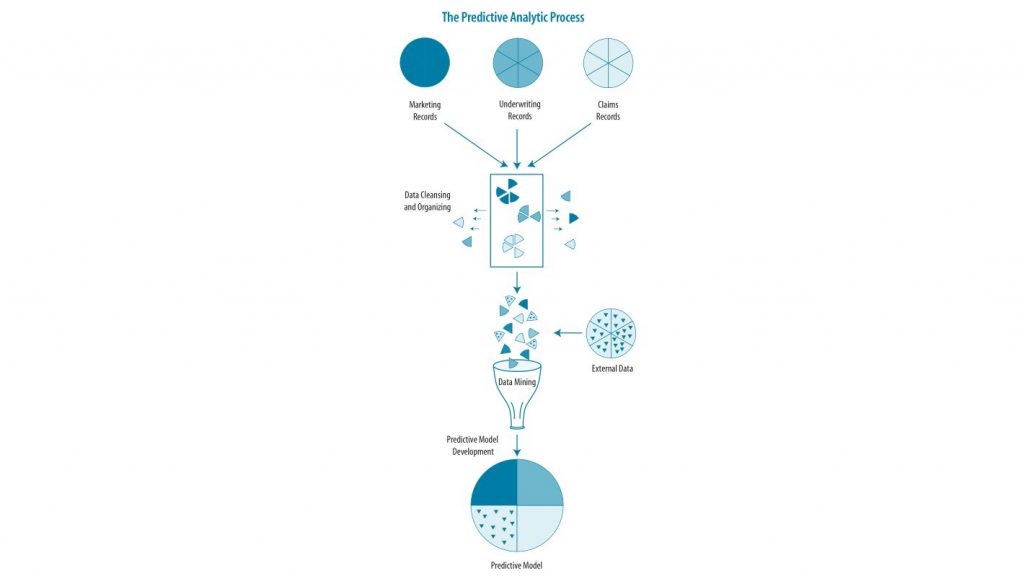
By analyzing data on plan participants’ health, lifestyle habits, and demographic characteristics, insurers can generate more precise estimates of life expectancy and potential benefit payouts. Moreover, the continuous stream of data from connected devices enables insurers to update these risk assessments in real-time.
AI-Powered Risk Management and Scenario Modeling
The explosion of data from connected devices also enables the development of more sophisticated AI-powered risk management and scenario modeling tools.
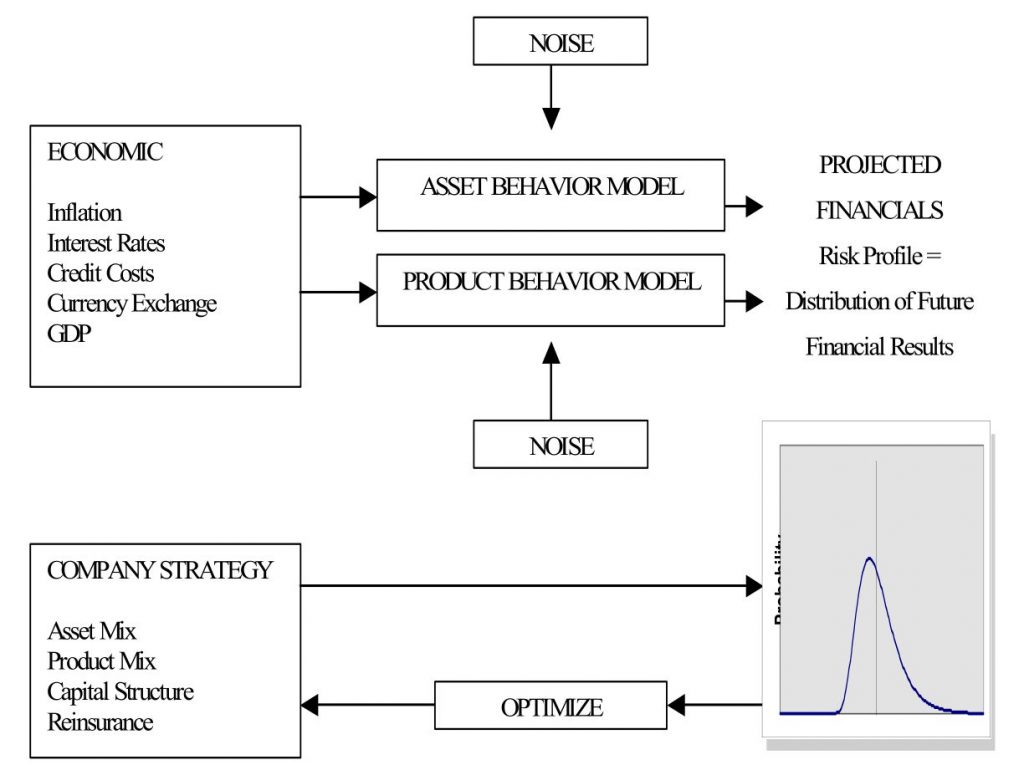
DFA (Dynamic Financial Assessment) Factor Model Schematic
For example, an insurer might use AI-powered scenario modeling to assess the potential impact of a major natural disaster on its property and casualty portfolio. By analyzing data on the location and characteristics of insured properties, as well as data on historical disaster patterns and climate trends, the insurer can generate more accurate estimates of potential losses and develop targeted risk mitigation strategies.
Beyond Basic Automation
AI and machine learning continue to redefine the insurance industry, moving beyond basic automation to enable deeper, more sophisticated insights and interactions.
Sophisticated Automated Underwriting
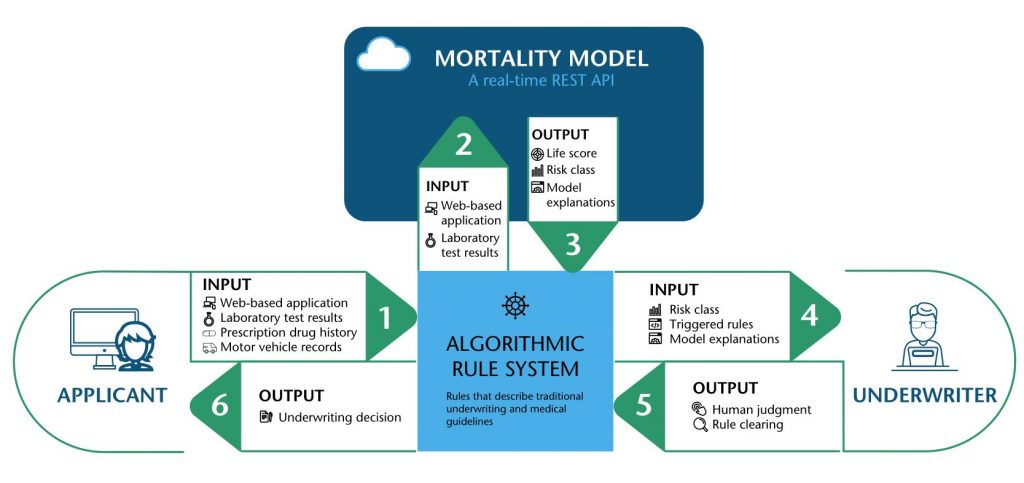
Algorithmic Underwriting System Schematic
Automated underwriting has transitioned from a time-saving automation tool to a complex, cognitive system that adapts and learns. Building on the vast amounts of data sourced from connected devices, AI systems now incorporate advanced machine learning algorithms that not only process applications but also predict future trends and policyholder behavior.
Enhanced Claims Processing with Cognitive AI
In claims processing, AI’s role has evolved from streamlining workflows to performing deep contextual analysis that mirrors human cognitive processes. By employing advanced NLP and computer vision, AI systems can interpret the context of claims data, recognize patterns of fraud, and even predict claim complexity and processing time.
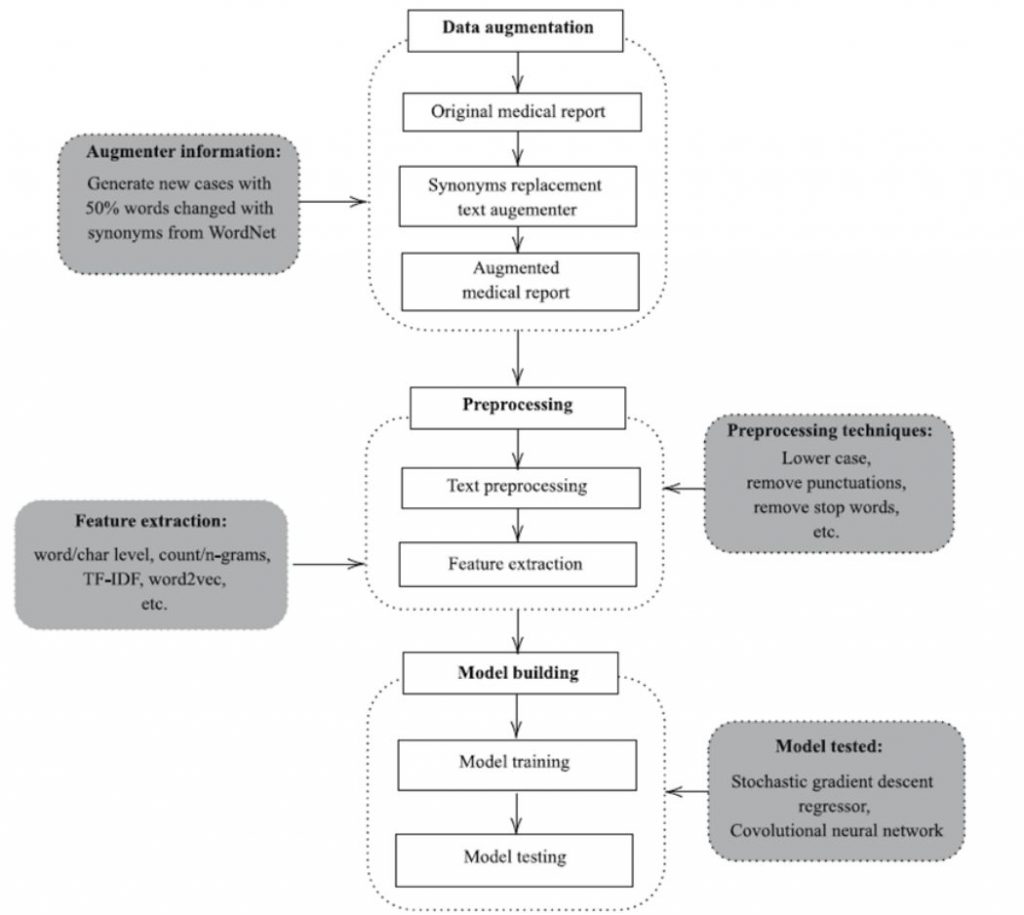
Framework for injury cost prediction using document analysis
This level of analysis was once the domain of human experts but is now being augmented by cognitive AI, leading to faster, more accurate claims resolutions.
Deep Learning For Unstructured Data
Deep learning has moved from analyzing unstructured data to understanding and interacting with it in inherently cognitive ways. In property and casualty insurance, for instance, deep learning models analyze satellite imagery not just to assess current property conditions but also to predict potential future risks based on environmental changes.

Detection results of proposed vehicle damage estimator
In health insurance, these models process medical images to not only identify current health issues but also predict possible future medical conditions, enabling insurers to offer preventative solutions tailored to individual risk factors.
The Rise of Automation and Robotics
As the insurance industry embraces more sophisticated technologies, automation and robotics are playing increasingly crucial roles in transforming operations, product offerings, and risk assessment methods.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is revolutionizing back-office operations in insurance by automating routine and repetitive tasks. This technology not only streamlines processes but also significantly reduces the likelihood of manual errors. Advanced forms of RPA integrate cognitive technologies, including machine learning and natural language processing, enabling them to handle complex tasks that traditionally require human judgment.
For instance, cognitive RPA can automatically interpret communication from clients, categorize it, and route it to the appropriate department or even resolve common issues without human intervention.
Autonomous Vehicles and Their Transformative Impact on Auto Insurance
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles (AVs), particularly at automation levels 4 and 5, presents significant challenges for the insurance industry, broadly categorized into legal and market determinants. Legally, the primary concern revolves around liability for damages in the event of accidents.
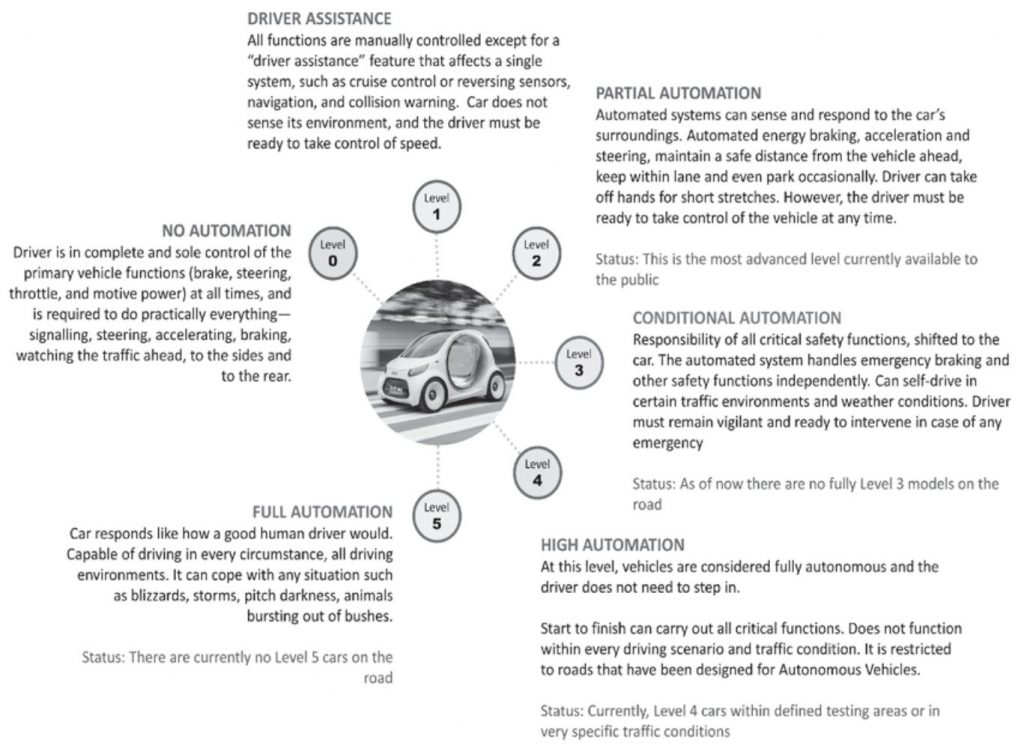
Historically, human error—stemming from factors like inattention and fatigue—has been the predominant cause of road accidents. However, as vehicles become fully autonomous, the human role diminishes from driver to mere passenger, fundamentally altering the liability landscape. The liability may shift from individuals to manufacturers or software providers, requiring new legal frameworks to address complex scenarios where AVs must make critical decisions, such as choosing between lesser evils in unavoidable crash situations.
Market-wise, the implications are profound. The enhanced safety promised by AVs could reduce the incidence of accidents, potentially diminishing the motor vehicle insurance market. This shift may drastically alter traditional business models, replacing personal Third Party Liability (OC) insurance with new forms designed for AV transport solution providers, likely resulting in a much smaller market. Moreover, insurers must navigate emerging risks like cybersecurity threats, which could involve hacking or sabotage of AV systems. The transition also means insurers need to develop new pricing models based on whether a car is human-driven or computer-operated, simultaneously exploring new revenue streams as personal expenditures on car ownership and operation decrease.
Drones and Claims Processes
Drones equipped with advanced sensors, such as thermal imaging and LIDAR, are enhancing the accuracy of property risk assessments and claims processing. These technologies allow insurers to detect issues invisible to the naked eye, such as poor insulation or water leaks, and predict areas at risk of future damage. Drones expedite the claims process, particularly in hard-to-reach areas affected by natural disasters, by providing real-time data to claims adjusters.
Robotics are also transforming customer service within the insurance industry. AI-powered chatbots and virtual agents are being increasingly used for handling claims and inquiries, providing 24/7 customer service. This not only improves efficiency but also enhances customer experience by offering instant support and reducing wait times.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies
The integration of blockchain and distributed ledger technologies (DLT) is set to profoundly reshape the insurance industry by enhancing data security, transparency, and efficiency. These technologies facilitate a decentralized and tamper-proof framework.
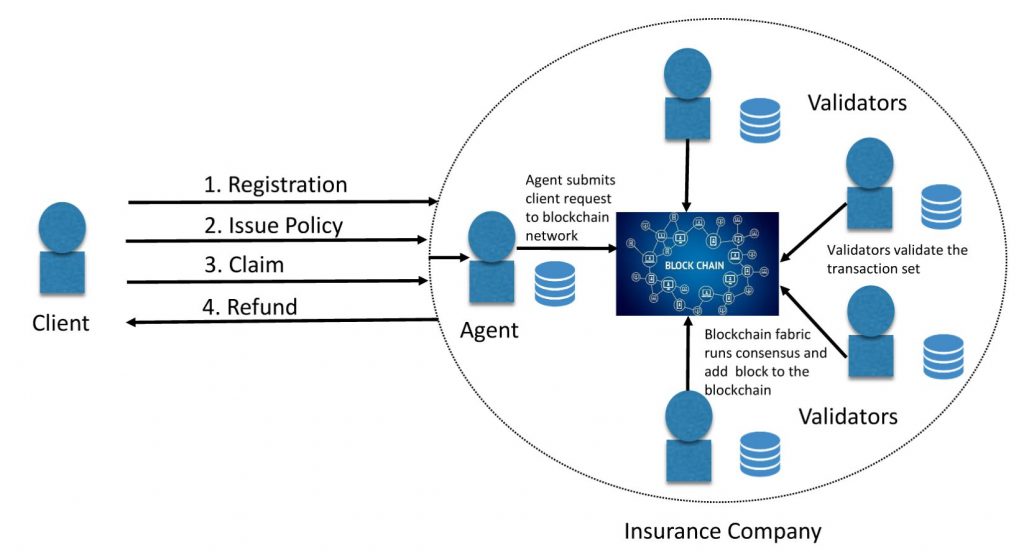
Insurance Blockchain Framework
By providing a shared, immutable ledger, blockchain ensures that all parties have access to consistent and unalterable data. For instance, in complex transactions involving multiple parties, such as international reinsurance contracts, blockchain can provide a single source of truth that all entities can rely upon, thus reducing the need for costly reconciliation processes.
Reducing Fraud and Enhancing Trust
Blockchain’s inherent properties of transparency and immutability also play a significant role in reducing fraud and enhancing trust in insurance transactions. Each transaction recorded on a blockchain is validated by the network, making unauthorized data alterations nearly impossible.
This not only helps in mitigating common forms of insurance fraud, such as false claims and premium diversion but also strengthens the trust between insurers and policyholders. Enhanced trust leads to better customer relations and potentially more stable insurance markets as consumers feel more secure in their transactions.
Smart Contracts for Automating Policy Administration
One of the most impactful applications of blockchain in insurance is the use of smart contracts for automating policy administration. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. These contracts automatically enforce and execute the terms of agreements based on predefined rules and triggers.
For example, in the event of a claim that meets certain verifiable conditions, a smart contract can automatically process and settle the claim without human intervention, thereby streamlining policy issuance, renewals, and claims settlement.
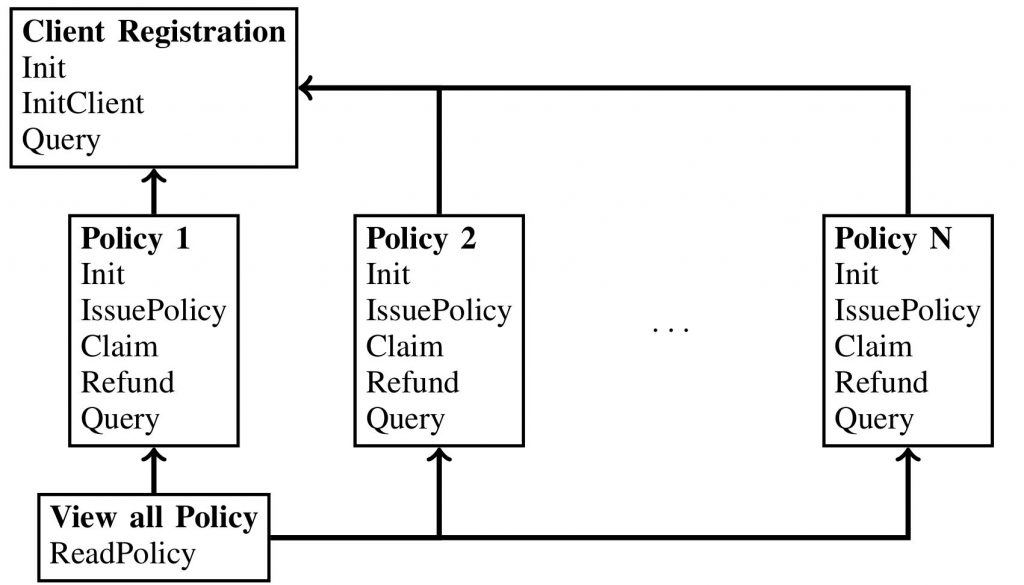
This automation significantly reduces administrative costs and improves operational efficiency. It minimizes the likelihood of errors and delays in processing, which are common in traditional manual handling. Additionally, it provides policyholders with a faster, more transparent service, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Surfing the AI Wave: How Insurers Can Stay Ahead
As the AI wave swells, insurers need to get ready. Preparing for AI is not just about technological upgrades. It is about building a culture that embraces innovation while navigating the ripples of change.
Invest in AI Literacy
First, fostering AI literacy across the organization is crucial. From the C-suite to customer service, understanding AI’s capabilities and limitations empowers employees to make informed decisions and fosters an environment where AI tools are used effectively. Regular training sessions, workshops, and hands-on projects can demystify AI, turning apprehension into appreciation.
Attracting and retaining the right AI talent is critical. Insurers need to bring on board individuals with expertise in AI, data science, and machine learning to drive innovation and translate complex algorithms into actionable business strategies.
Data, Data Everywhere
Next, insurers must ensure their data houses are in order. AI is only as good as the data it consumes. By cleaning, organizing, and securing their data, insurers can feed their AI systems with high-quality inputs, leading to more accurate and reliable outputs. This includes investing in robust data management systems and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation(GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Ethical AI Governance
Creating a framework for ethical AI use is non-negotiable. This involves setting up governance structures that review and monitor AI applications for ethical implications, ensuring that AI solutions adhere to principles of fairness and non-discrimination.
Collaborative Innovation
Lastly, embracing a collaborative approach can amplify the benefits of AI. This means not only internal collaboration across departments but also external partnerships with tech firms, startups, and academic institutions. Such collaborations can provide fresh insights, foster innovation, and speed up the adoption of advanced AI technologies.
Conclusion
The triumph of AI in insurance will not be gauged by the intricacy of the algorithms or the sheer volume of data processed. It will be measured by the indelible impact it leaves on people’s lives. By harnessing AI to make insurance more accessible, affordable, and attuned to individual needs, insurers hold the power to effect meaningful change in the world.
And that’s a future worth embracing with open arms.



