You can sense the transformation rippling across the group benefits industry. Employee demographics now span five generations, mental health challenges are on the rise, and personal finances have grown more precarious than ever. Meanwhile, 40% of employers are boosting their investment in benefits innovation to stay competitive (SHRM, 2023). At the same time, tech-savvy startups are compelling legacy carriers to redefine what “employee benefits” ought to deliver.
But it is no longer enough to hand out a standard health plan and a predictable retirement package. Today’s workforce wants more – coverage that aligns with the realities of their lives, mental health resources they can actually use, and a sense that their employer is committed to their total well-being. If insurers want to keep up, they need to adapt, and quickly. In this article, we will explore the most significant trends reshaping group benefits, from flexible plan structures to AI-powered platforms, and examine why embracing these new solutions is critical to remaining relevant and driving long-term success.
On-Demand Insurance and Flexible Coverage
Rigid, one-size-fits-all group plans are disappearing. This is the age of on-demand insurance – coverage that employees can activate or adjust in real time, often through a mobile app. Initially popular with gig workers (such as ride-hail drivers needing short-term coverage) on-demand insurance is now making its way into group benefits. According to Allied Market Research, the global on-demand insurance market could exceed USD 23.7 billion by 2032, growing at an estimated 12.5%. Employees increasingly expect their benefits to be as flexible as the digital services they use daily, and insurers are responding with new platforms designed for real-time customization.
One compelling example is Surest (formerly Bind), an on-demand health plan model that allows employees to “dial up or down” coverage throughout the year instead of waiting for annual enrollment. In early pilots, Surest cut healthcare costs by 10–15% for employers while giving workers more control over their coverage. The model eliminates complex deductibles and coinsurance structures, replacing them with transparent, upfront pricing, so employees know their costs before scheduling care. By simplifying plan administration and guiding members to cost-effective providers, on-demand insurance benefits both insurers and employers.
Startups are also pushing this trend forward. Demandoo, for example, offers “on-demand global insurance” that can be activated or deactivated based on an employee’s activity – even for part-time, seasonal, or contract workers. Originally designed for gig platforms, this usage-based model has gained traction among employers looking to reduce spending on underutilized benefits while offering employees exactly the coverage they need.
For group benefits insurers, on-demand coverage is a massive competitive advantage. It supports modern work arrangements, caters to diverse employee needs, and helps control costs. As hybrid and project-based employment models continue to grow, demand for ultra-flexible benefits will only increase.
Customizable Health Plans
Static health plans are falling out of favor. More than half of employers (51%) say they are actively seeking innovative plan designs or curated provider networks to contain costs while maintaining quality (Mercer, 2023). The result? A push toward more flexible, consumer-centric health coverage.
One example is Aetna’s SimplePay, which replaces deductibles and coinsurance with straightforward copays for all services. Early results showed a 12% reduction in total healthcare costs for employers that adopted it. Similarly, UnitedHealthcare’s Surest plan features a “buy-up” model that allows employees to add coverage tiers for specific procedures when needed. Employees in Surest plans have reported 54% lower out-of-pocket expenses than those in traditional plans.
With a multi-generational workforce, demand for customization is only increasing. Instead of offering one static plan, many employers now provide a menu of coverage levels, provider networks, and supplemental benefits tailored to employees’ life stages. For insurers, this represents a key opportunity to create differentiated, data-driven products that align with today’s demand for transparency and choice.
Integrated Wellness Programs
Workplace wellness programs have evolved far beyond gym reimbursements and step challenges. The global wellness market is projected to reach USD 13.3 trillion by 2033, up from USD 6 trillion in 2023. This growth reflects an expanded definition of well-being—one that includes mental health, stress management, and financial wellness. A meta-analysis by Baicker et al. found that medical costs decrease by approximately $3.27 for every dollar spent on worksite wellness programs.
Major insurers have embraced this shift. Vitality, for instance, uses wearable devices and app-based platforms to reward employees for healthy behaviors like exercise, preventive screenings, and balanced nutrition. In Asia and North America, AIA and John Hancock have launched similar programs, offering discounts on premiums and additional coverage for employees who meet wellness milestones.
Beyond physical health, modern wellness programs now incorporate mental health coaching, nutritional counseling, sleep tracking, and stress management tools. Many insurers partner with digital health startups to offer telehealth therapy, meditation apps, and guided resilience training. As awareness of the connection between well-being and productivity grows, these benefits have moved from optional perks to essential components of employer-sponsored plans.
Financial Wellness Solutions
Money-related stress is a productivity killer. A 2022 PwC survey found that 73% of employees cite personal finances as their greatest source of stress—outranking both job-related and health concerns (PwC, 2022). This financial anxiety leads employees to delay care, skip prescriptions, or underutilize their health benefits, ultimately increasing costs for insurers and employers alike.
The Growth of Financial Wellness Programs
- By 2023, the number of employers offering/expanding financial wellness benefits had grown to 86% according to some reports. This trend has continued to move upwards since.
- The U.S. financial wellness market was valued at USD 618 million in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 1.89 billion by 2028, growing at over 20% annually.
Types of Financial Wellness Solutions
- Budgeting and Debt Management: Digital platforms like BrightPlan, Financial Finesse, and Enrich offer personalized financial coaching and spending analysis.
- Student Loan Assistance: With U.S. student loan debt surpassing USD 1.7 trillion, some insurers now offer employer-sponsored repayment and refinancing programs.
- Emergency Savings Plans: Payroll-deducted emergency savings accounts, often employer-matched, help employees avoid high-interest debt.
By proactively addressing financial stress, insurers improve benefits engagement, reduce claim costs, and position themselves as essential partners in employee well-being.
Digital Platforms and AI-Driven Benefits
Technology is now at the center of how benefits are designed, delivered, and experienced. As employers seek more efficient, user-friendly ways to manage benefits, insurers are responding with digital platforms and AI-driven tools that offer personalization, real-time decision support, and deeper data insights. According to Mercer’s 2023 Global Talent Trends report, nearly half of HR budgets are now allocated to technology investments, with benefits administration platforms among the top priorities.
These platforms go far beyond automating enrollment. They provide dynamic, intuitive interfaces where employees can compare plans, receive tailored recommendations, and manage benefits year-round (often via mobile apps or integrated web portals). AI-powered decision support tools can analyze claims history and usage patterns to help employees select the most cost-effective coverage. Some tools even project out-of-pocket costs based on likely utilization, enabling smarter decision-making.
Behind the scenes, insurers are using predictive analytics to optimize plan design, improve underwriting, and manage claims more proactively. An overwhelming majority of insurers are currently using or planning to use AI in their benefits operations, with applications ranging from claims analytics to service automation.
AI chatbots and virtual assistants are also becoming integral to modern benefits infrastructure. These tools handle routine inquiries, alleviate HR workloads, and provide employees with 24/7 support. For example, Allianz’s virtual assistant “Allie” reportedly resolves up to 80% of customer queries without human intervention. Similar bots are now being used by employers to assist with enrollment, explain plan features, and support claims navigation.
Equally important is the ability of digital platforms to integrate seamlessly with other parts of the workforce ecosystem. Many insurers now offer API-based platforms that connect with payroll systems, telehealth services, wellness apps, and financial tools creating a unified digital experience. The rise of embedded benefits, where insurance offerings are integrated directly into broader employee platforms, is further driving convenience and efficiency.
Perhaps the most transformative shift is toward hyper-personalization. With data from wearables, wellness apps, biometric screenings, and claims histories, insurers can deliver highly targeted recommendations. An employee who recently became a parent might be prompted to explore supplemental life insurance. Another who is increasing physical activity could be nudged toward wellness incentives. What once felt generic now feels tailored, and that’s exactly what employees expect.
For group benefits insurers, digital transformation is the foundation of a modern, competitive offering.
Mental Health Coverage and Wellness
Anxiety, burnout, isolation – these are not abstract concepts. They are showing up in inboxes, performance reviews, and claims data. Employers are feeling the strain of a workforce that’s more emotionally taxed than ever, and insurers are being called to respond.
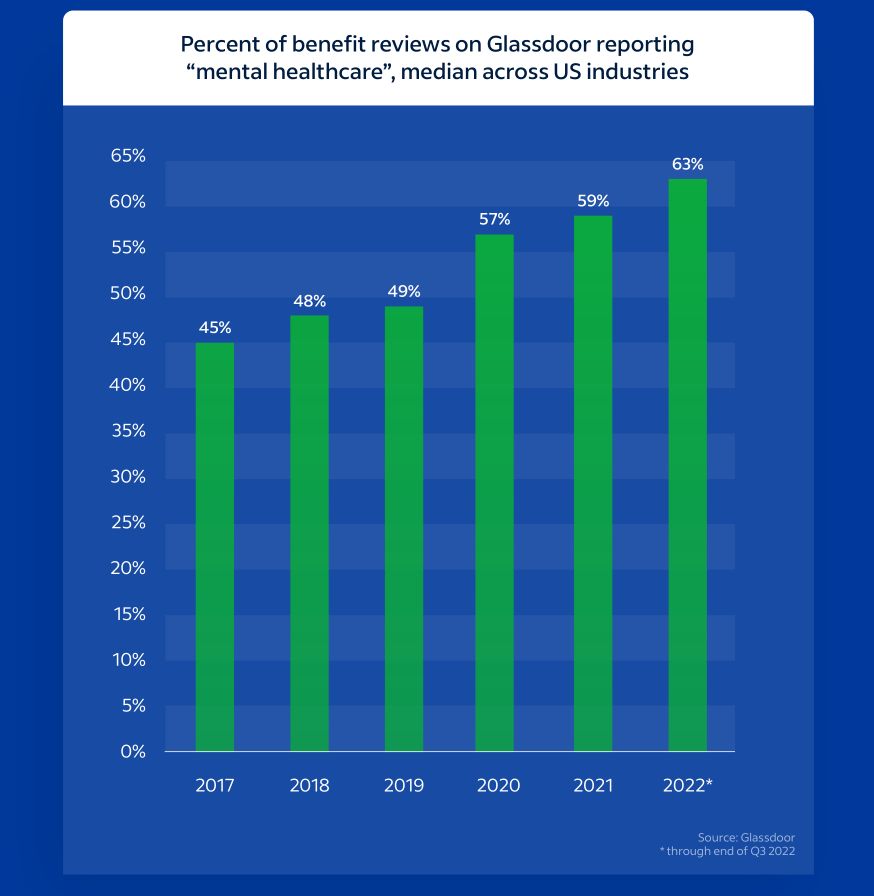
What was once considered a peripheral perk has become a core pillar of employee benefits strategy. Mental health support is now a baseline expectation. A 2023 SHRM survey found that 89% of employers offer mental health coverage, up from 84% just a few years earlier. This shift reflects not only changing cultural attitudes, but also a growing recognition of the business impact. Mental health issues are directly tied to absenteeism, lower productivity, and higher healthcare costs.
Insurers have responded by expanding access points and broadening their mental health offerings. Traditional options like therapy sessions and Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) are now complemented by teletherapy platforms, meditation apps, mental health coaching, and AI-enabled triage tools. According to Glassdoor, 66% of employees reported in 2023 that their employer offers mental health benefits, and 71% of those employees have actively used them.
That level of engagement has been driven by easier access, especially through digital channels. Teletherapy adoption surged during the pandemic, and many insurers have since made it a permanent part of their offerings. Employees can now schedule therapy sessions, use 24/7 chat counseling, or access self-guided cognitive behavioral therapy, often embedded in their benefits platforms.
But access alone is not enough. Employers and insurers are investing in preventive mental health strategies to tackle issues before they escalate. These include mindfulness training, stress resilience coaching, mental health “first aid” certifications, and manager education programs. A 2024 survey by Wellable found that 91% of employers plan to increase investment in mental health support, and 66% are expanding stress management initiatives.
Still, network adequacy remains a challenge. Only 67% of large employers feel confident that their plans provide sufficient access to in-network mental health professionals. To bridge that gap, insurers are expanding provider networks, increasing reimbursement rates, and partnering with digital mental health startups. Some are even deploying internal telehealth teams to provide faster, more consistent access to care.
Culture changes also matter. Many employers now run mental health awareness campaigns, train managers to recognize signs of distress, and integrate mental wellness into broader well-being programs. These initiatives help reduce stigma and encourage employees to seek care early.
Globally, the momentum is growing. In regions like Asia and Latin America, where mental health support has traditionally been limited, insurers are increasingly adding mental health riders to group medical plans. Regulatory mandates around mental health parity are further pushing insurers to treat psychological care with the same priority as physical care.
For insurers, the opportunity is clear. Deliver more than coverage. Deliver impact.
Other Emerging Benefit Trends
As workforce needs diversify, insurers are expanding beyond conventional offerings to deliver more inclusive, holistic benefit solutions. What was once considered fringe—fertility support, pet insurance, lifestyle spending accounts—is rapidly moving into the mainstream.
Fertility and Family-Building Benefits
Fertility support is one of the fastest-growing areas of group benefits. In 2023, 40% of U.S. employers offered some form of fertility benefit, up from 30% in 2020. Among large employers, coverage for in vitro fertilization (IVF) has nearly doubled since the early 2000s. Insurers are responding by bundling fertility coverage with adoption assistance, surrogacy support, and maternity care navigation, thus meeting the needs of younger, diverse, and family-oriented workforces.
Parental Leave and Eldercare Support
Employers are also expanding leave policies and caregiving benefits. At the same time, eldercare support is gaining ground, driven by the “sandwich generation” caring for both children and aging relatives. Services like backup care stipends, referral assistance, and caregiving navigation are appearing in more group packages.
Pet Insurance
Pet insurance, once a novelty, is now a top voluntary benefit. The global pet insurance market is expected to grow from $9.18 billion in 2024 to $10.7 billion in 2025 at a CAGR of 16.5%. In 2023, 19% of U.S. employers offered pet insurance, up from 14% the year before, according to some reports. While employee-paid, this benefit resonates with the 70% of U.S. households that own a pet and provides employers with a low-cost, high-appeal perk.
Lifestyle Spending Accounts (LSAs)
LSAs are another rising trend. These employer-funded stipends allow employees to spend on wellness-related expenses—fitness memberships, mental health apps, nutrition coaching, or even creative hobbies. In 2024, 52% of employers reported either offering or evaluating LSAs as part of their benefits strategy. For insurers, LSAs present opportunities to integrate flexible, employee-directed spending into broader wellness ecosystems.
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)-Oriented Benefits
Benefits aligned with DEI priorities are also gaining momentum. Insurers are helping employers offer gender affirmation coverage, floating cultural holidays, and access to alternative therapies. 69% of executives rate diversity and inclusion (whether based on caregiving status, age, gender identity, or cultural background) as an important issue, indicating a high level of support from leadership. Inclusive benefits not only support diverse talent but help insurers build differentiated, value-aligned products.
Regulatory-Driven Innovation
Legislation is also driving new benefit models. The Washington Cares Fund, the first state-run long-term care insurance program in the U.S., mandates LTC coverage through payroll deductions. This has sparked renewed interest in private LTC coverage and led many employers to reconsider benefit offerings. Globally, mental health parity laws, telehealth reimbursement mandates, and EU work-life balance directives are pushing insurers to expand coverage and develop more adaptable, compliance-ready products.
Group benefits are no longer just about coverage. They are about supporting people’s lives in full. And insurers who can meet those needs holistically will be the ones who lead the next chapter of the industry.
Conclusion
The group benefits landscape is evolving rapidly. Employees want on-demand coverage, personalized health plans, financial security, and integrated wellness solutions. And employers are turning to insurers for help meeting those needs.
The most competitive carriers are no longer just selling policies. They are building ecosystems. They are using AI, data, and strategic partnerships to create holistic, human-centered benefits that go beyond traditional insurance.
To stay ahead, insurers must
- Offer modular, flexible plans tailored to diverse workforces.
- Leverage AI and analytics for smarter, more intuitive benefits.
- Expand partnerships with fintech, wellness, and care delivery providers.
- Design inclusive benefits that reflect today’s workforce realities
In a talent market where benefits are a differentiator, a promise, and a competitive edge, forward-thinking insurers have an opportunity not just to keep up, but to lead.



