Imagine telling an insurance executive in the 1970s that, in the not-so-distant future, they would be crafting group benefit plans that include coverage for mindfulness app subscriptions, pet insurance, or even student loan repayment assistance. They might have chuckled at the absurdity—or marveled at the complexity. Yet here we are in 2024, navigating a landscape where insurers are at the forefront of innovating employee benefits, transforming them into a strategic tool for employers in the battle for top talent.
But when did this transformation truly take hold, and what forces are propelling it forward? It’s challenging to pinpoint an exact moment. Perhaps it was the rise of Silicon Valley’s tech giants, whose demand for cutting-edge benefits pushed insurers to expand their offerings. Or maybe it was the global pandemic that forced us to rethink risk models and accelerated the adoption of digital health solutions. What is clear is that the traditional group benefit plan—once a predictable mix of health insurance, a retirement plan, and perhaps basic life coverage—has evolved into something far more complex and personalized.
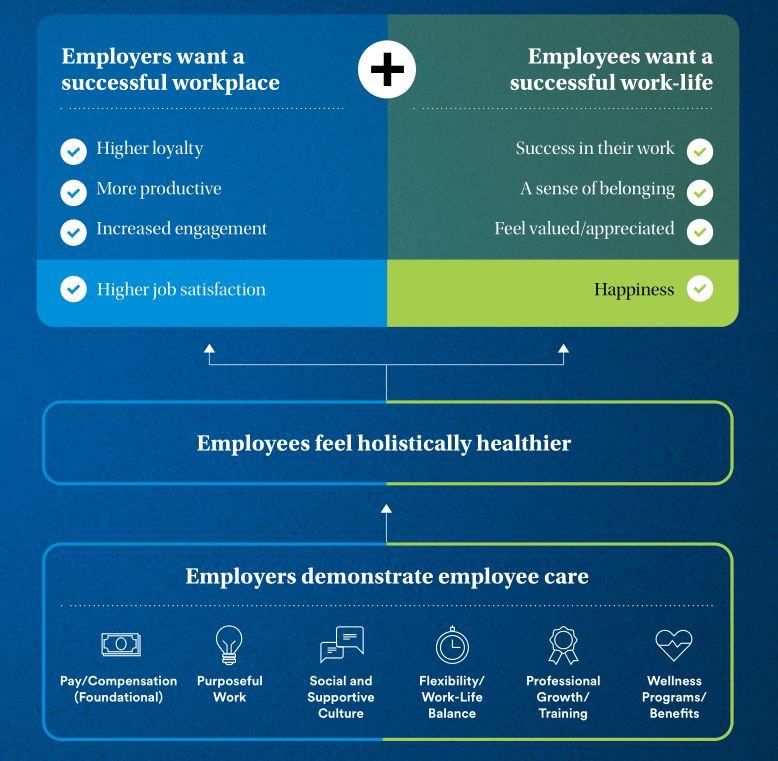
The trends shaping group and employee benefits in 2024-25 present both opportunities and challenges for insurers.
Labor Market Conditions
The technology sector anticipates a significant talent gap, with some projections estimating a shortfall of hundreds of thousands of skilled professionals in the next few years. Moreover, the rise of the gig economy has transformed traditional employment models. Recent studies suggest that freelancers and contract workers now comprise over a third of the U.S. workforce—a trend accelerated by the global shift toward remote work.
This shift necessitates portable benefits that cater to non-traditional employment arrangements.
Impact of Inflation and Rising Healthcare Costs
Inflation and escalating healthcare costs present a dual challenge that cannot be ignored. Employers are under immense pressure to control expenses, while employees increasingly seek comprehensive coverage to offset the rising cost of living. For insurers, one strategy gaining traction is the implementation of value-based care models. Insurers like UnitedHealthcare have partnered with providers to focus on patient outcomes rather than the volume of services rendered. This approach has reportedly led to a reduction in hospitalizations by 12%.
Changing Workforce Demographics and Expectations
The workforce is undergoing a significant demographic shift. Millennials and Gen Z now make up a significant of the global workforce. These generations prioritize personalization, digital integration, and social responsibility in their employment experience.
Companies like Aetna are expanding mental health support by offering access to mindfulness apps, virtual therapy sessions, and stress management programs.
Personalized and Flexible Benefits
In a landscape where 79% of employees value the ability to customize their benefits, the traditional one-size-fits-all approach is swiftly becoming antiquated.
Modern benefits administration platforms, powered by AI and machine learning, enable real-time tailoring of benefit offerings. Data analytics provide insights into employee preferences, allowing for the design of products that resonate on an individual level. For instance, MetLife’s MyBenefits portal offers a user-friendly interface where employees can select from a diverse array of benefits, ranging from traditional health insurance to more niche offerings like legal services and pet insurance.
However, this flexibility introduces complexities in underwriting. To mitigate this, insurers are adopting strategies like pooled risk models and tiered pricing.
Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs)
With the IRS raising the annual FSA contribution limit to $3,200 for 2024, flexible spending accounts are garnering renewed interest.
By integrating FSAs with health plans and offering comprehensive educational resources, insurers can demystify these accounts. Companies like HealthEquity have built platforms that allow seamless management of FSAs, HSAs, and HRAs, providing a holistic view of an employee’s health finances.
Convertible Paid Time Off (PTO)
The concept of convertible PTO is gaining traction. Employees appreciate the flexibility to tailor their benefits to their personal circumstances—whether that means taking additional time off or boosting their financial security.
Insurers can innovate by offering products that integrate with these PTO policies. For instance, employees might convert unused PTO into contributions toward their 401(k) plans, health savings accounts, or purchase additional life or disability insurance coverage.
However, navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial. The IRS treats PTO cash-outs as taxable income, and there are strict guidelines governing these transactions. Additionally, labor laws like the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) impose requirements that must be adhered to.
Mental Health and Well-being Focus
The growing emphasis on mental health presents both a need and an opportunity for insurers to expand coverage and services.
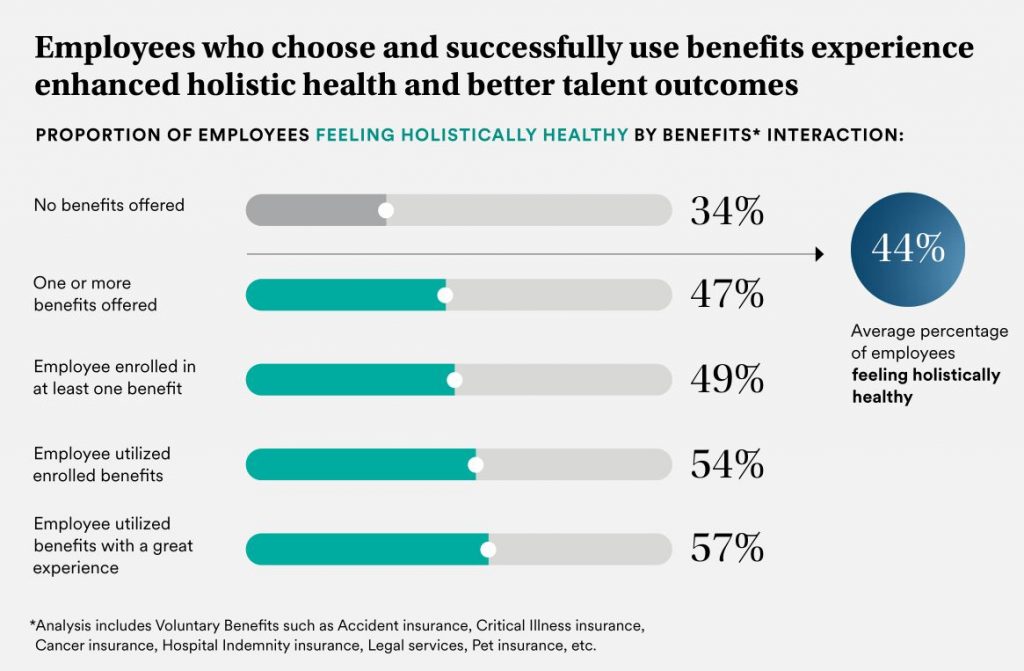
Expanded Mental Health Coverage
With approximately 20% of adults experiencing mental illness each year, as reported by the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), the demand for accessible mental health services is undeniable. The World Health Organization estimates that depression and anxiety disorders cost the global economy $1 trillion annually in lost productivity.
Regulatory developments like the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) require insurers to offer mental health benefits on par with medical and surgical benefits.

Insurers are responding by broadening their mental health networks and incorporating innovative solutions. For example, Blue Cross Blue Shield’s collaboration with Quartet Health integrates physical and mental healthcare, facilitating referrals and care coordination.
Stress Management and Resilience Programs
Workplace stress remains a pervasive issue. This not only affects individual well-being but also has tangible business impacts, including increased absenteeism and higher healthcare costs.
Insurers are uniquely positioned to offer stress management and resilience programs that deliver measurable ROI. A Harvard study found that for every dollar spent on wellness programs, medical costs fell by approximately $3.27, and absenteeism costs fell by about $2.73.
Collaboration with employers is essential. Insurers can provide communication materials, host webinars, and offer incentives to encourage participation.
Work-Life Balance Initiatives
While employers set the policies that govern work-life balance, insurers can play a supportive role by offering benefits that encourage healthy lifestyles beyond the workplace.
For instance, insurers might offer premium discounts or rewards points for participation in health challenges, gym memberships, or preventive care activities. Employee assistance programs (EAPs) provide confidential counseling services for personal or work-related issues, supporting employees in managing stress and maintaining balance.
Financial Wellness Programs
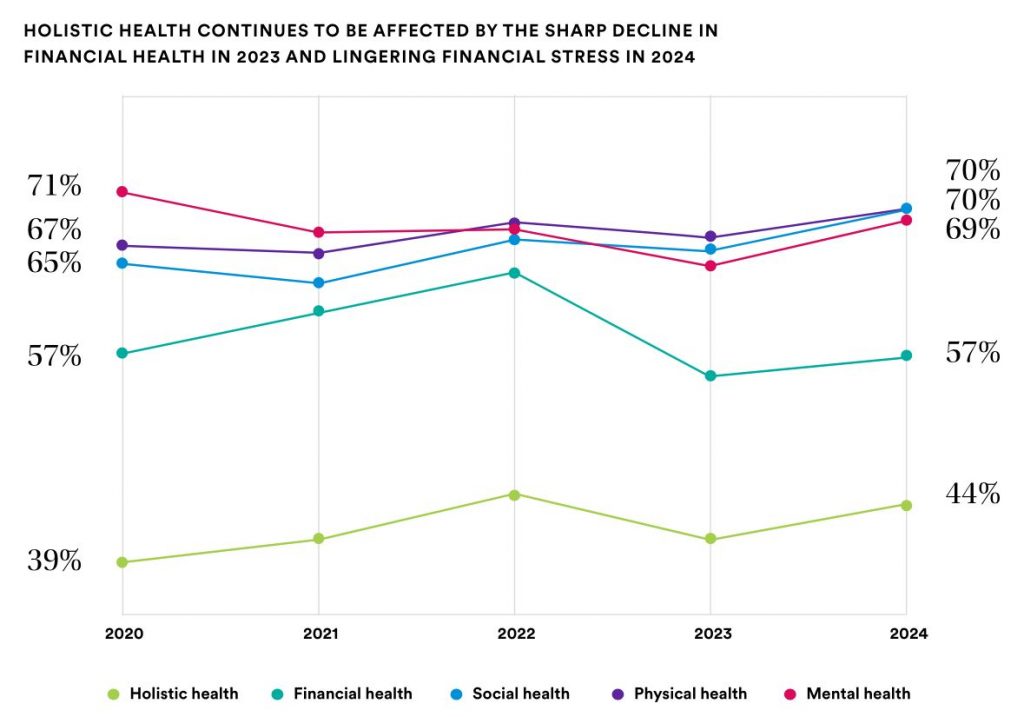
Financial stress can be a significant burden, affecting not just employees’ personal lives but their productivity at work. For insurers, this represents an opportunity to develop programs that address these concerns.
Retirement Savings Support
The reality of insufficient retirement savings looms large for many employees. A report by the Federal Reserve indicates that nearly 25% of Americans have no retirement savings at all, and among those who do, the median savings for those nearing retirement age is alarmingly low. This retirement readiness gap presents a critical challenge—and opportunity—for insurers.
To address this, insurers are enhancing their retirement plan offerings with innovative features. Auto-enrollment and auto-escalation have become industry best practices, significantly increasing participation and contribution rates. Vanguard’s “How America Saves” report shows that plans with automatic enrollment boast participation rates of over 90%, compared to just 67% in voluntary enrollment plans.
Student Loan Repayment Assistance
With U.S. student loan debt surpassing $1.7 trillion, the financial strain on employees—particularly Millennials and Gen Z—is substantial. The average borrower carries about $ thirty thousand in student loan debt, which can delay milestones like home ownership or retirement savings.
Recognizing this burden, insurers are developing programs to facilitate employer-sponsored student loan repayment assistance.
For instance, Prudential Financial in partnership with Greenpath offers a student loan assistance program program that allows employers to make direct contributions to employees’ loan balances, coupled with personalized counseling and budgeting tools.
Financial Education and Counseling
Financial literacy remains a significant challenge, with the FINRA Investor Education Foundation reporting that two-thirds of investors could not pass a basic financial literacy test.
Insurers are addressing this gap by offering comprehensive financial education and counseling services as part of their benefits packages.
Healthcare Cost Management
Balancing comprehensive coverage with cost control is a critical challenge for insurers.
High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
HDHPs paired with HSAs have gained significant traction as a cost-management strategy. According to the National Center for Health Statistics, enrollment in HDHPs rose to 51% of all insured employees in 2023, reflecting a steady upward trend. These plans offer lower premiums, making them attractive to cost-conscious employers and employees alike.
HSAs provide a tax-advantaged way for employees to save for medical expenses. Funds roll over year to year, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.
However, HDHPs come with challenges. High out-of-pocket costs can lead some individuals to delay or forego necessary care, potentially resulting in more severe health issues and higher costs down the line. To address this, insurers are designing HDHPs with features like first-dollar coverage for preventive services and value-based insurance design (VBID) elements.
Telemedicine and Virtual Health Options
The adoption of telemedicine has accelerated dramatically, with McKinsey reporting a 38-fold increase in telehealth utilization since before the COVID-19 pandemic. This surge reflects a shift in both provider offerings and patient preferences, solidifying telemedicine as a staple in healthcare delivery.
Preventive Care Emphasis
Preventive care remains a cornerstone of effective healthcare cost management. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that up to 90% of healthcare spending is attributable to chronic conditions and mental health management.
A study by RAND Corporation found that employers investing in comprehensive wellness programs experienced an average ROI of $1.50 for every dollar spent, primarily through reduced healthcare expenditures.
Flexible Work Arrangements
The shift toward remote and hybrid work models has been one of the most significant workplace transformations in recent history. This trend is expected to continue, driven by employee demand for flexibility and technological advancements enabling remote collaboration.
Insurers can support this shift by
- Offering Cybersecurity and Data Protection Insurance: Remote work increases exposure to cyber risks. Insurers like Chubb have developed policies that protect against data breaches, phishing attacks, and other cyber threats, providing coverage for both employers and employees.
- Providing Ergonomic Support Programs: To prevent musculoskeletal disorders associated with improper home office setups, insurers can offer resources and assessments. For instance, Liberty Mutual provides virtual ergonomic evaluations and personalized recommendations to promote safe work environments.
Four-Day Workweek Pilots
The concept of a four-day workweek has gained momentum, with companies across the globe experimenting with reduced working hours without salary cuts. A trial in Iceland involving over 2,500 workers resulted in maintained or increased productivity and improved employee well-being, as reported by the Association for Sustainability and Democracy (ALDA).
Enhanced Family and Caregiving Support
As employees increasingly value work-life balance, expanded parental leave has become a key component of competitive benefits packages. Insurers can advise on structuring leave benefits that align with organizational goals and comply with legal requirements.
From a regulatory standpoint, compliance with the FMLA and state-specific laws is essential. Some states, such as California and New York, have mandated paid family leave programs with specific provisions that insurers must incorporate into their products.
Childcare Benefits and Subsidies
Childcare expenses can consume a significant portion of household income, with the Economic Policy Institute reporting average annual costs exceeding $9,000 per child in the U.S. This financial strain can affect employee productivity and retention.
Insurers can support employers by stepping in proactively.
- Offering Dependent Care FSAs: These allow employees to set aside pre-tax dollars for eligible childcare expenses, reducing taxable income. The IRS sets the annual contribution limit at $5,000 for individuals or married couples filing jointly.
- Providing Childcare Subsidies or Vouchers: Insurers can facilitate programs where employers subsidize a portion of childcare costs, often in partnership with childcare networks.
Elder Care Support
With the U.S. Census Bureau projecting that by 2030, one in five Americans will be over the age of 65, the need for elder care support has become increasingly pressing. Many employees find themselves part of the “sandwich generation,” caring for both children and aging parents.
Elder care support addresses a critical need in today’s workforce. Insurers that provide these benefits enable employees to balance their professional and personal lives more effectively, resulting in a more engaged and stable workforce.
Professional Development and Career Growth
In a rapidly evolving job market, continuous learning and career advancement opportunities have become indispensable for attracting and retaining top talent. Insurers can support employers by integrating professional development benefits into their offerings, aligning with organizational goals and employees’ aspirations.
Learning and Development Programs
A striking 94% of employees, as highlighted in LinkedIn’s Workplace Learning Report, express a willingness to stay longer with an employer that invests in their professional development. This presents insurers with a significant opportunity to enhance their group benefit offerings.
Insurers can facilitate learning and development by
- Partnering with Educational Platforms
- Customizing Training Solutions
- Supporting Professional Certifications
Tuition Reimbursement
The escalating cost of higher education remains a significant barrier for many seeking to advance their qualifications. With average tuition fees increasing by over 30% in the past decade, employees are increasingly valuing tuition assistance as a key benefit. A recent study found that 60% of employees indicated they would choose a job offering strong tuition reimbursement.
Insurers that incorporate these programs help employers cultivate a more skilled and committed workforce.
Physical Wellness Initiatives
Harvard University research indicates that employers save an average of $3.27 in medical costs for every dollar invested in wellness programs. Recognizing this, insurers are offering comprehensive physical wellness solutions that not only reduce healthcare expenses but also promote a healthier, more productive workforce.
Humana’s Go365 program exemplifies success in this area, rewarding members for engaging in healthy behaviors like regular exercise and preventive screenings. Participants have shown reduced healthcare claims and improved overall well-being.
Financial Wellness Support
Financial stress is a pervasive issue affecting a significant portion of the workforce. According to PwC’s Employee Financial Wellness Survey, 60% of employees report being stressed about their finances, which can negatively impact productivity and engagement. Insurers are stepping in to alleviate this burden through comprehensive financial wellness programs.
Prudential’s Pathways program is a noteworthy example, delivering financial wellness solutions that have led to improved financial behaviors among employees.
Technology-Driven Benefits Administration
Artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced analytics are transforming the insurance industry. AI and analytics enable insurers to deliver more tailored and efficient services. Embracing these technologies is essential for staying competitive in today’s market.
Employees expect the convenience of managing their benefits on-the-go, prompting insurers to develop mobile-friendly platforms.
Insurers can enhance mobile engagement by
- Developing Comprehensive Mobile Apps: Apps that allow users to view plan details, submit claims, find in-network providers, and access digital ID cards. UnitedHealthcare’s Health4Me app is a prime example, offering a wide range of services.
- Focusing on User Experience (UX): Ensuring that mobile platforms are intuitive and easy to navigate. This includes streamlined interfaces, clear information architecture, and responsive design.
Conclusion
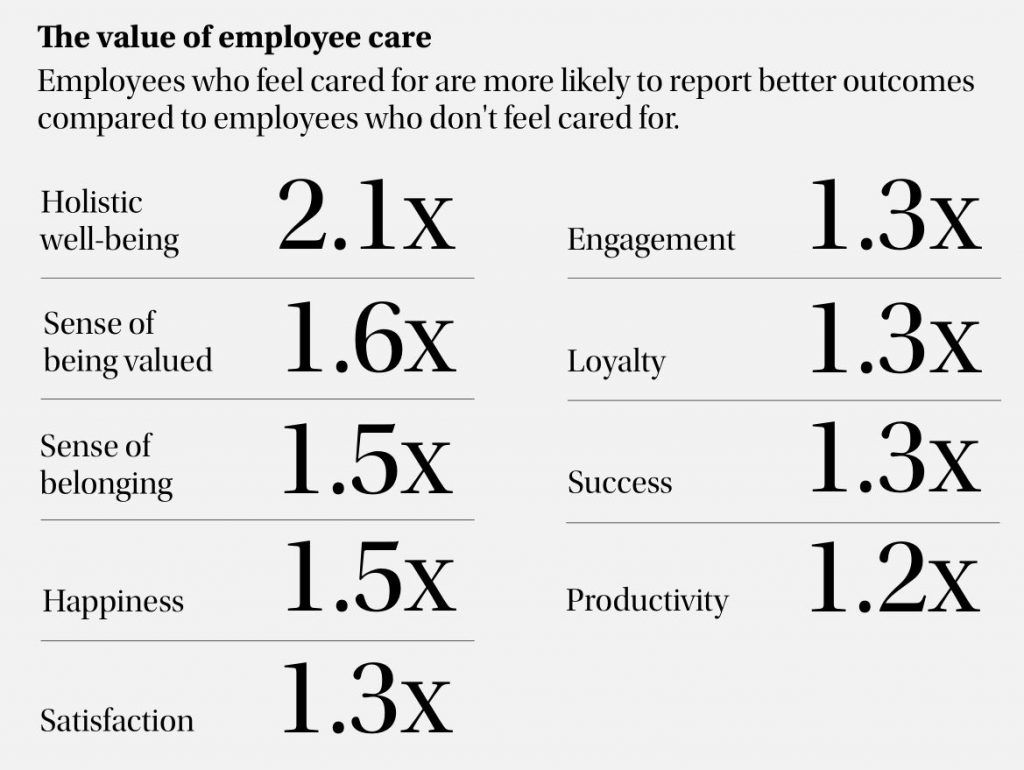
As we reflect on the varied trends shaping group and employee benefits in 2024-25, one theme emerges prominently: the imperative for insurers to adapt and innovate. From embracing technology and holistic wellness to addressing diverse workforce needs and navigating complex regulations, insurers are at the forefront of transforming the employee benefits arena.
By leveraging data, fostering personalization, and committing to continuous improvement, insurers can craft benefit solutions that not only meet the current demands of employers and employees but also anticipate future shifts. In doing so, they reinforce their pivotal role in enhancing the well-being of the workforce and driving organizational success.



