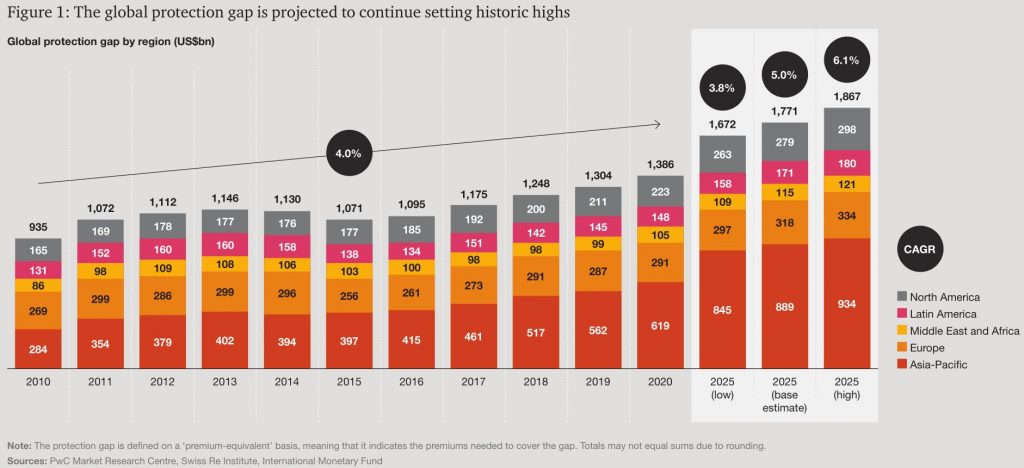
The insurance industry stands at a crossroads. The global protection gap, a measure of uninsured risk, looms large. By 2025, it will reach $1.86 trillion. This is not just a number. It represents real people and businesses exposed to financial ruin. The old models of insurance are failing to keep pace with a rapidly changing world. Climate change, cyber threats, and shifting demographics present new challenges. We need new solutions.
In this challenging landscape, insurtech innovations offer a critical pathway to the future of insurance. The integration of artificial intelligence, blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced data analytics offers tangible solutions to the industry’s most pressing problems. These technologies are not abstract concepts but practical tools already reshaping how insurance is underwritten, sold, and managed.
In this article, we will explore some transformative Insurtech trends in detail, examining their potential impact and potential to shape the very foundations of insurance.
Embedded Insurance
At its core, embedded insurance integrates coverage directly into the purchase process of products and services, making it an inherent part of the customer’s buying journey rather than a separate transaction.
This trend goes beyond simply offering insurance at the point of sale. It is about seamlessly weaving insurance into everyday transactions and experiences. For instance, when you book a vacation, travel insurance could be automatically included. Or when you buy a new smartphone, device protection could be built into the price. McKinsey projects that embedded insurance could grow to a $270 billion market in Asia by 2030.
Parametric Insurance
Unlike traditional insurance that compensates for actual loss incurred, parametric insurance pays out a predetermined amount based on the occurrence of a specific, measurable event.
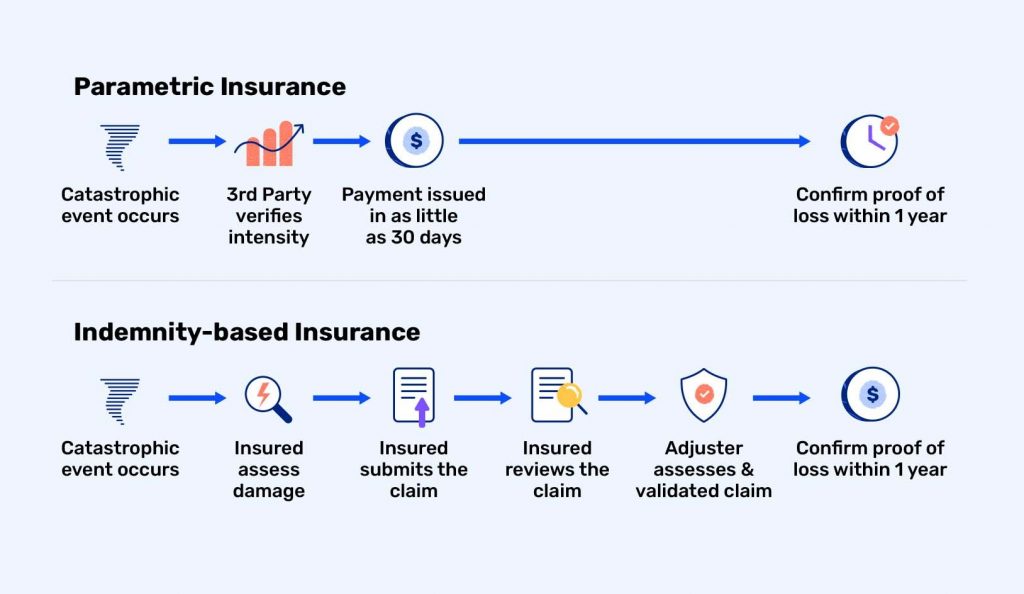
This innovative approach is particularly well-suited for our increasingly data-rich, connected world. For example, in the realm of climate risk, a parametric policy might automatically trigger a payout if wind speeds exceed a certain threshold during a hurricane, or if rainfall falls below a specified level for crop insurance. The beauty of this model lies in its simplicity and speed – there is no need for lengthy claims assessments or disputes over damage valuations.
Companies like Etherisc are already pioneering this approach with flight delay insurance that uses smart contracts to automate payouts based on real-time flight data. As we move towards 2025, expect to see parametric insurance expand into new areas, driven by the proliferation of IoT devices and sophisticated data analytics.
GenAI for P&C Insurance
The power of generative AI, exemplified by tools like Gemini, Claude and GPT-4, is being leveraged to automate and enhance various aspects of the insurance value chain, from underwriting and claims processing to fraud detection and customer support.
In the P&C sector, generative AI is particularly poised to transform claims operations. Many insurers are focusing their initial AI adoption efforts on claims, given the quicker return on investment this area tends to offer. For instance, AI can rapidly analyze images of property damage, assess repair costs, and even detect potential fraud, significantly speeding up the claims process.
Moreover, AI-powered chatbots can provide instant, 24/7 customer service, handling routine inquiries and guiding policyholders through the claims process. We can expect to see more sophisticated applications of generative AI in P&C insurance, such as personalized policy recommendations and real-time risk assessment. Some estimates suggest that embedded insurance could account for over $700 billion In GWP by 2030 (25% of the total market).
Investments in Insurtech will continue to grow
The insurtech sector is experiencing a remarkable surge in investment. This influx of capital is reshaping the very foundations of the insurance industry, bringing in fresh perspectives and cutting-edge technologies.
The global insurtech market revenue was valued at $5.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 52.7% from 2023 to 2030.
While North America continues to lead in insurtech investments, other regions are gaining ground:
- Asia-Pacific: Fastest-growing market, with a projected CAGR of 39.1% from 2023 to 2030
- Europe: Seeing increased activity, particularly in the UK and Germany
What is particularly intriguing is that much of this capital is coming from outside the traditional insurance industry – from entrepreneurs, digital giants, and innovators from other sectors who see the potential to revolutionize this age-old industry.
Cybersecurity Risk Assessment Improvements
The digital transformation of businesses across all sectors has exponentially increased their vulnerability to cyber threats, creating both challenges and opportunities for the insurance industry.
Insurers are developing increasingly sophisticated cybersecurity risk assessment tools, leveraging machine learning to identify vulnerabilities, predict potential threats, and provide actionable insights to mitigate risks. These advanced tools go beyond traditional risk assessment methods, analyzing patterns in customer data and claims history to detect potentially fraudulent activities with unprecedented accuracy. The global cyber insurance market is expected to reach $20 billion by 2025.
Companies at the forefront of this trend are leveraging AI/ML for comprehensive risk assessment:
- Beazley: Uses machine learning to analyze clients’ IT infrastructure and identify vulnerabilities.
- CrowdStrike: Employs AI-powered threat intelligence for real-time risk assessment.
- Coalition: Utilizes proprietary data and ML algorithms for continuous monitoring and risk evaluation
Customer Centric Digital Transformation
insurers are increasingly focusing on creating seamless, omnichannel experiences that cater to the evolving expectations of digital-native consumers. According to the Gartner CIO Survey, 87% of insurance CIOs reported an increase in the use of digital channels to reach customers during the pandemic, a trend that is expected to accelerate. This shift encompasses everything from AI-driven chatbots for 24/7 customer service to mobile apps that allow policyholders to manage their coverage, file claims, and receive real-time updates.
Companies like Lemonade are leading the charge, using AI to process claims in seconds and provide instant policy quotes. This paradigm shift encompasses a holistic approach to understanding and meeting customer needs. Insurers are investing in data analytics to gain deeper insights into customer behavior and preferences, enabling them to offer more personalized products and services.
Self-Service Portals for Policyholders
Industry-wide, there is a striking shift in consumer preferences – the number of people willing to switch insurance providers due to the lack of a user-friendly customer portal has increased dramatically. In response, a vast majority of insurers now offer policy management capabilities via mobile apps, with custom insurance applications becoming the preferred channel for customer servicing. These self-service platforms are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering features such as automated workflows, tailored dashboards, electronic signatures, and integrated knowledge bases.
For instance, some portals now allow customers to easily file claims, track their status in real-time, and even access instant quotes for additional coverage. This trend is particularly pronounced among younger demographics, who show a significant preference for digital channels in their insurance interactions.
Advanced Process Automation and Virtualization
Digital twins, which are dimensionally accurate 3D models, are revolutionizing risk assessment and claims management in the insurance sector. Our sources indicate that these virtual replicas provide insurers with a comprehensive view of risks and assets, allowing them to predict future vulnerabilities and develop proactive risk management plans. For instance, creating a digital twin of a property can help in predicting maintenance needs before they escalate into larger issues, potentially preventing claims. In claims management, digital twins enable more accurate and cost-effective assessments by allowing insurers to virtually inspect damages without physical site visits.
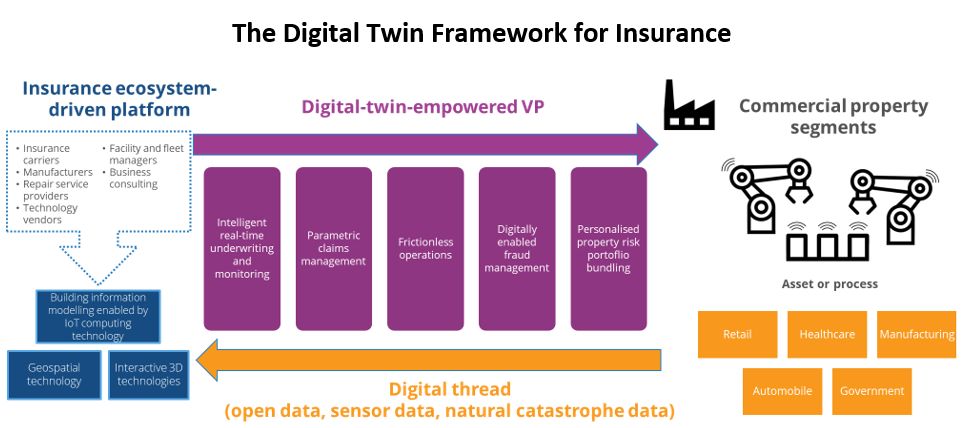
Similarly, 3D/4D printing technologies are being utilized for efficient claims processing and new product development. Insurers can use these technologies to quickly create parts or models needed for claims resolution, speeding up the process and improving customer satisfaction.
Ai for predictive analytics and underwriting
AI and machine learning algorithms are enabling insurers to analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, including telematics, wearables, and even social media, to create more accurate risk profiles. For instance, in auto insurance, telematics data can be used to assess driving behavior and offer personalized premiums based on actual usage and risk. Estimates indicate that automated underwriting can reduce operational costs by up to 30-50%, while significantly speeding up the process. Companies like Zurich Insurance are already implementing AI-powered platforms to streamline underwriting, enhancing both efficiency and accuracy.
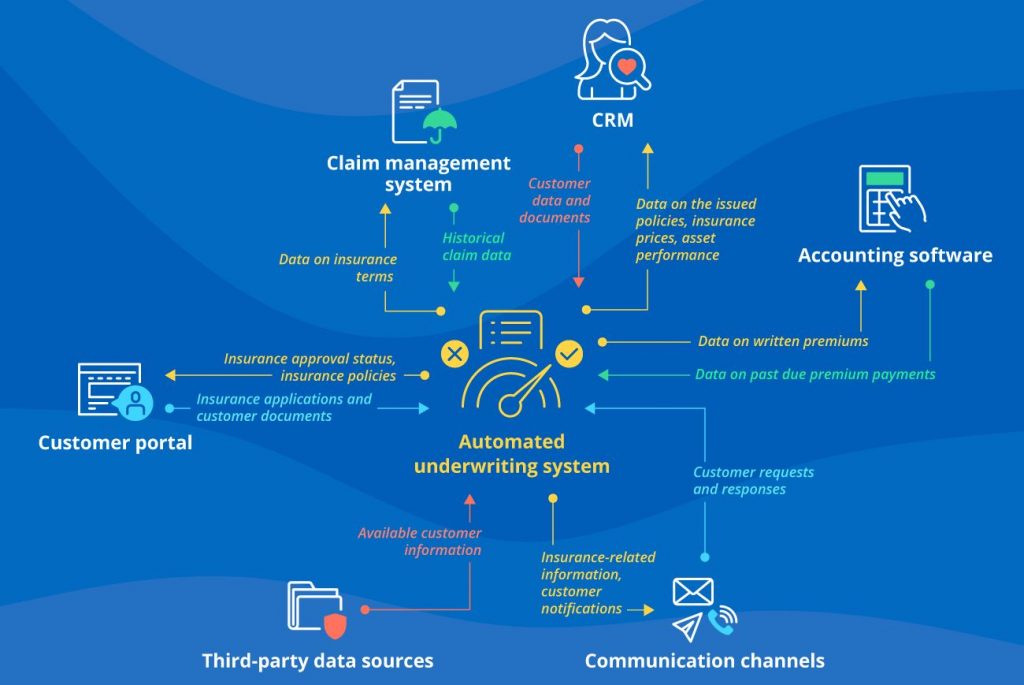
Moreover, predictive analytics is allowing insurers to move beyond reactive models to more proactive approaches. By leveraging AI, insurers can predict claim likelihood, identify fraud patterns, and even anticipate customer needs.
API driven partnerships and digital ecosystems
These ecosystems allow for seamless data sharing and collaboration between insurers, tech companies, and other service providers, enabling the creation of more comprehensive and personalized insurance solutions. For example, insurers are leveraging APIs to integrate their services with digital platforms in adjacent industries like automotive, real estate, and healthcare.
The adoption of cloud-native, API- or microservices-based architecture is providing insurers with the agility and flexibility needed to engage in these multi-party ecosystems.
RPA for Enhanced Automation of Business Processes
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is being deployed to handle a wide range of back-office processes, including data entry, policy administration, claims processing, and customer service. For example, bots can automatically enter data, process transactions, and handle routine customer inquiries much faster and with fewer errors than their human counterparts.
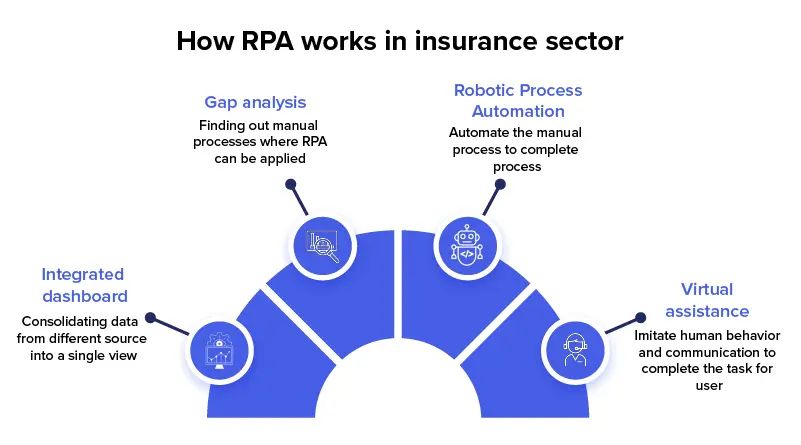
The impact of RPA on operational efficiency is substantial – a McKinsey report shows that robotic process automation return on investment in the first year ranges between 30% and 200%. In 2025 and beyond, we can expect to see more sophisticated RPA implementations in insurance, potentially incorporating AI and machine learning to handle increasingly complex tasks. This trend promises not only to reduce operational costs but also to improve accuracy, speed up processing times, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction by enabling faster, more efficient service delivery.
Voice activated insurance tech
Voice-activated insurance technology is expected to significantly enhance the customer experience. Customers will be able to easily access and modify their policies using voice commands, reducing the need for complex online navigation or phone calls. The technology will enable policyholders to report claims quickly and efficiently, potentially speeding up the claims process. Moreover, customers can get immediate answers to their insurance queries, improving satisfaction and reducing the load on customer service representatives.
AI-powered voice systems can also analyze customer data to offer tailored insurance product suggestions and coverage adjustments. The implementation of voice-activated technology offers substantial benefits for insurance companies as well. Automating routine inquiries and tasks can significantly lower operational costs and improve efficiency, as voice-activated systems can handle multiple customer interactions simultaneously.
IoT and Telematics
In the automotive sector, telematics devices are already tracking driving behavior, including speed, braking patterns, and route history. This real-time data enables insurers to offer personalized insurance plans that reflect individual driving habits, potentially rewarding safer drivers with lower premiums. The impact is significant – according to our sources, the global usage-based insurance market is projected to reach $66.94 billion by 2029, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 11.34% from 2024.
Beyond auto insurance, IoT devices are transforming property and health insurance. Smart home sensors can detect potential issues like water leaks or fire risks before they escalate into costly claims. In health insurance, wearable devices monitor physical activity and vital signs, allowing insurers to offer incentives for healthy behaviors. In the future, the proliferation of IoT devices will likely enable more dynamic, usage-based insurance models across various lines of business, shifting the industry from reactive coverage to proactive risk management and prevention.
Low code & No Code Platforms
Low-code/no-code (LC/NC) platforms are emerging as a significant trend in insurtech, revolutionizing how insurance companies develop and deploy digital solutions. These platforms are gaining traction rapidly, with Gartner estimating that by 2025, a staggering 70% of new applications will be built using LC/NC technology. This shift is driven by the need for faster digital transformation and improved operational efficiency in the insurance sector.
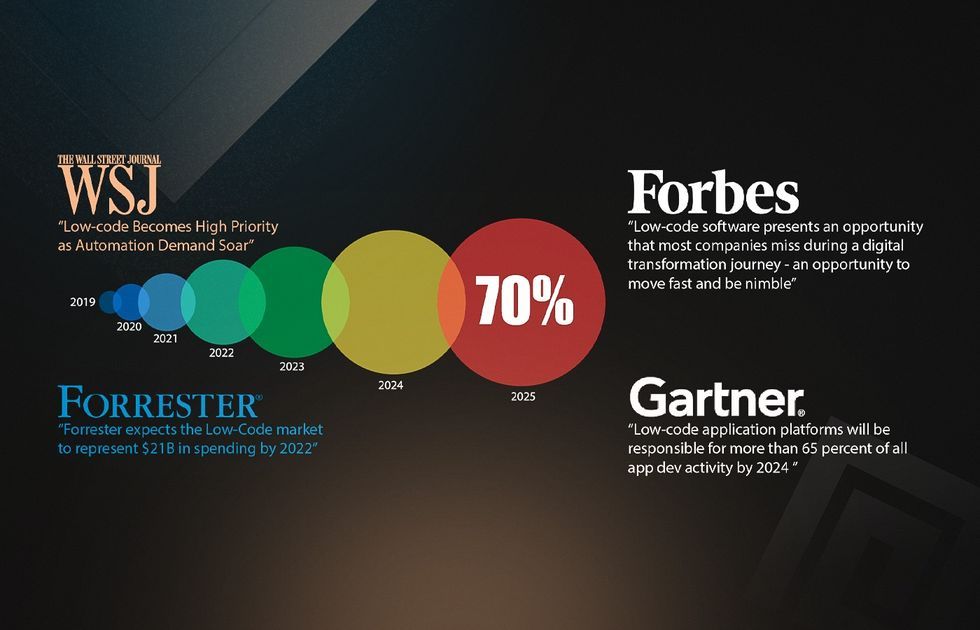
It accelerates the development and deployment of applications, reduces reliance on IT resources, and empowers business users to create solutions independently. This leads to improved customer experiences through faster product launches and more personalized services. Additionally, insurers can realize significant cost savings in application development and maintenance.
LC/NC platforms are being utilized for various purposes, including building quote journeys, creating automation rules, designing documents and email templates, configuring rates and underwriting rules, and developing customer portals and self-service applications.
Drones and Robotic Insurance Tech
Risk Assessment and Underwriting: Drones are increasingly used to conduct aerial surveys of properties, providing detailed imagery and data for more accurate risk assessment. This allows insurers to evaluate properties, especially in hard-to-reach or dangerous areas, without putting human inspectors at risk. The high-quality data collected by drones enables more precise underwriting and potentially fairer pricing of policies.
Claims Processing: After natural disasters or accidents, drones can quickly survey damaged areas, providing insurers with immediate, comprehensive visual data. This speeds up the claims process significantly, allowing for faster payouts and improved customer satisfaction. For instance, Allstate has reduced the time to produce repair estimates to just 4.5 days using drone technology.
Fraud Detection: The detailed imagery and data collected by drones can help insurers identify fraudulent claims more effectively. By having accurate before-and-after images of properties, insurers can better verify the extent and cause of damage.
Cost Reduction: By reducing the need for manual inspections, especially in hazardous or remote locations, insurers can significantly cut operational costs. PwC estimates that drones could help save the insurance industry nearly $7 billion per year through improved efficiency and reduced risk to human adjusters.
Enhanced Safety: Drones allow insurance professionals to assess dangerous areas or structures without physical risk, improving workplace safety for insurance employees. Data Analytics: The vast amount of visual and sensor data collected by drones can be analyzed using artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, providing insurers with deeper insights for risk management and policy decisions.
Conclusion
The insurtech trends we have explored are not merely technological advancements. They represent a fundamental reimagining of what insurance can be and how it can serve a rapidly changing world.
Yet, as we embrace these transformative technologies, we must remember that at its core, insurance is about people. It is about providing peace of mind, security, and support when it is needed most. The true measure of Insurtech’s success will not be in the sophistication of its algorithms or the efficiency of its processes, but in its ability to make insurance more accessible, affordable, and responsive to the needs of individuals and businesses around the globe.



